
Stablecoins are a special type of cryptocurrency designed to maintain a stable value by linking their price to another asset. Unlike Bitcoin (BTC) and other volatile cryptocurrencies, stablecoins aim to offer price stability, making them more practical for everyday transactions.
Why Are Stablecoins Important? 🔍

Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are known for extreme price fluctuations. For example, Bitcoin’s price surged from $5,000 in March 2020 to over $63,000 in April 2021, only to drop nearly 50% within two months!
While this volatility may be attractive to traders, it makes daily transactions risky. Imagine paying for a coffee with Bitcoin—its price might drop before the seller even processes the payment! Stablecoins solve this problem by keeping their value steady, making them more reliable for purchases and payments.
Stablecoins also serve as a bridge between the traditional financial system and the crypto world, allowing users to hold digital assets without worrying about sudden price swings.
Types of Stablecoins 🔢
There are four main types of stablecoins, each with its unique way of maintaining price stability.
1. Fiat backed Stablecoins 💴💶
These stablecoins are backed by traditional currencies like the U.S. dollar, Euro, or Yen. For every stablecoin issued, an equal amount of fiat currency is held in reserves by a trusted custodian. Popular examples include:
- Tether (USDT)
- TrueUSD (TUSD)
Since these coins are backed by real money, their value remains stable as long as the reserves are properly managed and audited.

2. Commodity-Backed Stablecoins 🟡🛢️⛽
Some stablecoins are pegged to physical assets like gold, silver, or oil. These commodities serve as collateral, offering an alternative to fiat-backed stablecoins. A well-known example is:
- Tether Gold (XAUt) – Pegged to the price of gold, providing crypto investors with a way to hold gold in digital form.
These stablecoins appeal to users who prefer assets with intrinsic value rather than fiat currency.
3. Crypto backed Stablecoins ₿🪙
Instead of using traditional currencies, these stablecoins are backed by other cryptocurrencies. Since crypto prices fluctuate, they are often over-collateralized to absorb price changes. A prime example is:
- Dai (DAI) – Managed by MakerDAO, this stablecoin is backed by Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies at a ratio of about 155%.
4. Algorithmic Stablecoins 🤖🔄
These stablecoins maintain their value without holding any reserves. Instead, they rely on smart contracts and algorithms to control supply and demand. If the price rises above the pegged value, the algorithm releases more coins to reduce the price. If it falls, the supply is reduced.
A famous (but now failed) example:
- TerraUSD (UST) – Once a top algorithmic stablecoin, it collapsed in 2022, leading to massive losses.
Algorithmic stablecoins are riskier than other types since they rely purely on market mechanisms.
How Do Stablecoins Work? ⚙️
Stablecoins achieve price stability through different mechanisms:
- Reserve Assets – Holding fiat, commodities, or crypto as collateral.
- Smart Contracts – Automating supply and demand adjustments.
- Trust and Audits – Regular audits ensure reserves match issued stablecoins.

Stablecoin Regulations: A Growing Concern 💼
As the stablecoin market grows (currently worth over $162 billion), regulators are paying closer attention. Governments worry about financial stability, fraud risks, and how these digital assets interact with traditional banking systems.
Regulatory Actions So Far:
- U.S. Regulation 🇺🇸 : Lawmakers propose stricter rules, including bank-like regulations for stablecoin issuers.
- European Union 🇪🇺 : The Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) bans algorithmic stablecoins and requires other stablecoins to maintain a 1:1 asset backing.
- Global Oversight 🌍 : The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) suggests regulating stablecoins like traditional financial institutions.
As regulations evolve, stablecoins may become more transparent and widely accepted.
Stablecoins vs. Bitcoin: What’s the Difference? 🌐
Stablecoins and Bitcoin serve different purposes:
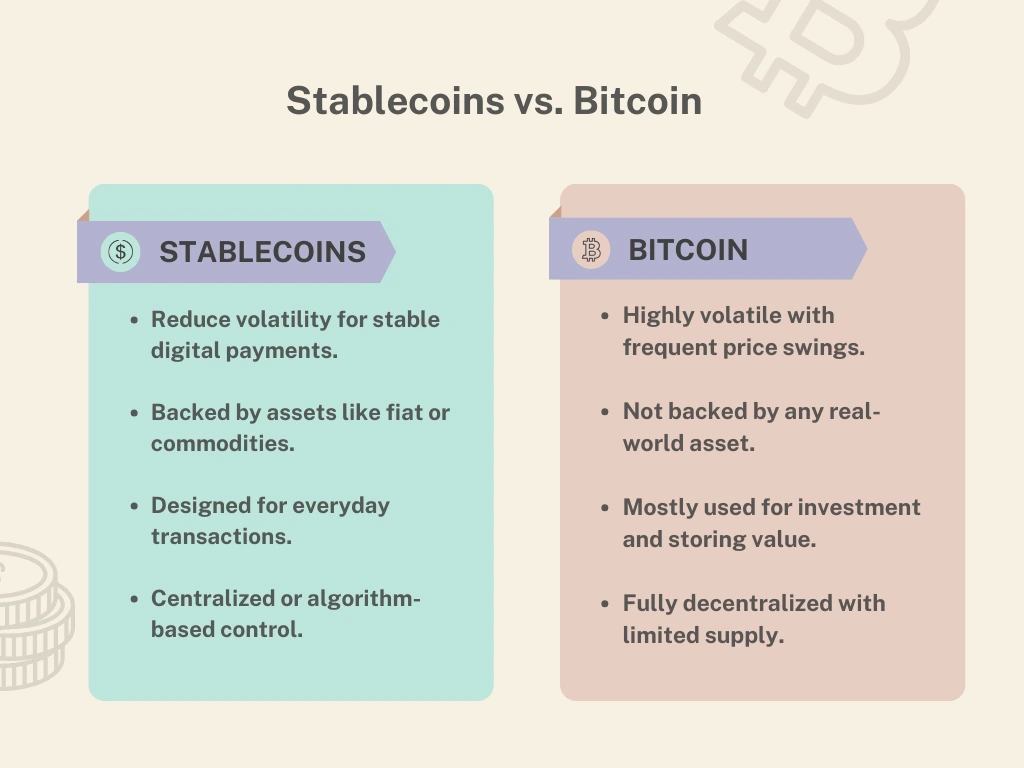
- Bitcoin (BTC) is a decentralized store of value with high volatility.
- Stablecoins offer price stability and are better suited for everyday transactions.
Both play an important role in the crypto ecosystem, but stablecoins provide a practical solution for payments and trading.
Which Is the Best Stablecoin? 💪
The most popular stablecoin is Tether (USDT), consistently ranked in the top five cryptocurrencies by market capitalization. It is widely accepted across exchanges like Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase.
Other solid choices include:
- USD Coin (USDC) – Backed by Circle and regularly audited.
- Dai (DAI) – A decentralized stablecoin backed by crypto assets.
Conclusion 📌
Stablecoins provide a much-needed solution to the crypto market’s volatility, making digital payments more reliable. Whether they are backed by fiat, commodities, or algorithms, they play a crucial role in the future of decentralized finance (DeFi).
However, as seen with past failures, users should research and choose stablecoins with strong transparency and backing. With regulations tightening, stablecoins may become a bridge between the crypto world and mainstream finance.
Stay ahead in crypto and forex trading—explore more insightful blogs at AlgoDeltaFX and unlock the secrets to successful trading!
What are your thoughts on stablecoins? Do they make cryptocurrency more practical for everyday use? Share your opinion in the comments! 💬📝
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and not financial advice. Always do your own research before investing.
source : investopedia

